最近和浩博讨论了下几道关于二分查找的题目。正好做一下总结,方便下一次能够快速手写出二分的算法。
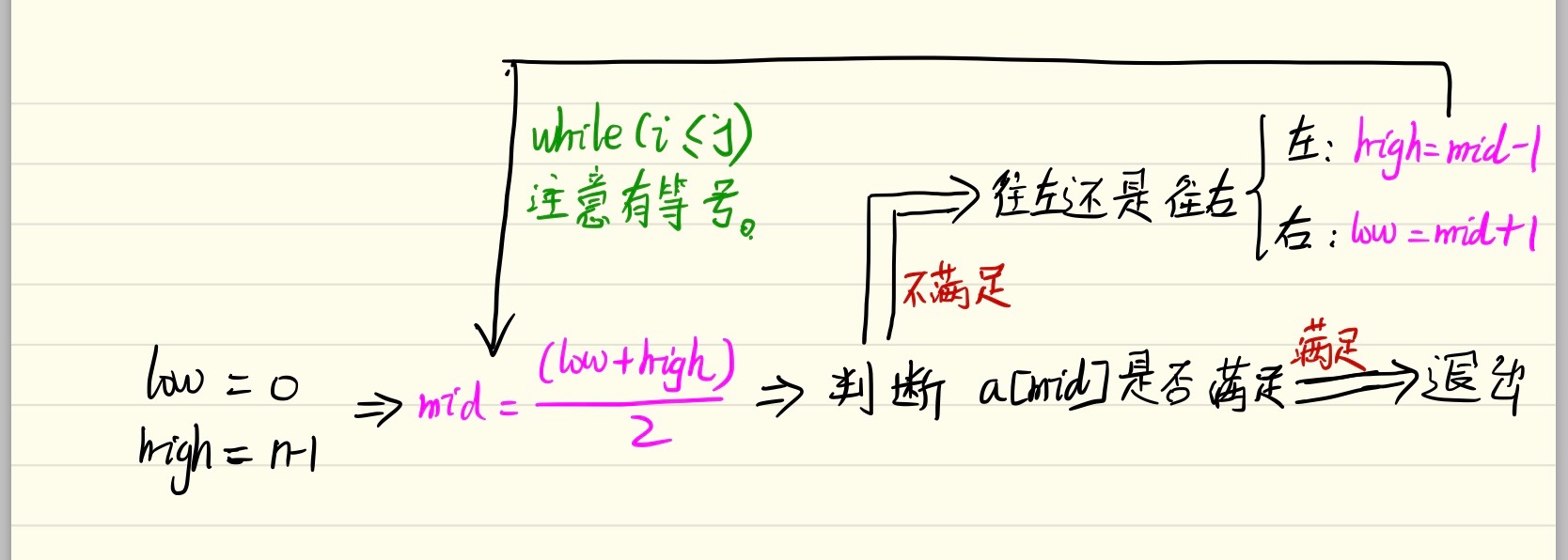
其实,二分查找,可以用下图简单表示流程。
最基本的二分查找:在一个递增的序列查找某个值。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14int len = nums.size();
int low = 0, high = len - 1;
int mid;
while (low <= high)
{
mid = low + (high - low) / 2;
if (nums[mid] == target)
return true;
else if (nums[mid] > target)
high = mid - 1;
else
low = mid + 1;
}
return false;
LeetCode 34. Search for a Range
Given an array of integers sorted in ascending order, find the starting and ending position of a given target value.
Your algorithm’s runtime complexity must be in the order of O(log n).
If the target is not found in the array, return
[-1, -1].For example,
Given[5, 7, 7, 8, 8, 10]and target value 8,
return[3, 4]. 找出相同元素的上界和下界索引。
跟基本二分相比,就是要改变判断是否找到了的条件,不再是简单的a[mid] == target 就可以搞定的了。所以就手写了lowMatch 和 highMatch两个辅助函数来判断是否找到要找的上界和下界。以及思考如果这一回没找到接下来应该向左走还是向右走的问题。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63class Solution {
public:
vector<int> searchRange(vector<int> &nums, int target)
{
vector<int> ans;
int low = 0, high = nums.size() - 1;
int mid;
int ans1 = -1, ans2 = -1;
while (low <= high)//找最低
{
mid = (low + high) / 2;
if (lowMatch(nums, target, mid))
{
ans1 = mid;
break;
} else if (nums[mid] < target)
low = mid + 1;
else// nums[mid]>=target
high = mid - 1;//即使相等,也一定在左边找
}
low = 0, high = nums.size() - 1;
while (low <= high)//找最高
{
mid = (low + high) / 2;
if (highMatch(nums, target, mid))
{
ans2 = mid;
break;
} else if (nums[mid] <= target)//由上一个条件,即使跟target相等也不符合了
low = mid + 1;
else //nums[mid]>target
high = mid - 1;//mid有可能是解
}
ans.push_back(ans1);
ans.push_back(ans2);
return ans;
}
bool lowMatch(vector<int> &nums, int target, int i)
{
if (nums[i] != target)
return false;
if (i == 0)//第0个肯定是最左边的
return true;
else if (nums[i] != nums[i - 1])
return true;
return false;
}
bool highMatch(vector<int> &nums, int target, int i)
{
if (nums[i] != target)
return false;
if (i == nums.size() - 1)//最后一个肯定是最右边的
return true;
else if (nums[i] != nums[i + 1])
return true;
return false;
}
}; 其实这道题用STL模板库的lower_bound和upper_bound会更加简洁,但也少了锻炼自己手写二分的能力。(一开始就是用STL做的0-0)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20class Solution {
public:
vector<int> searchRange(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
vector<int>::iterator low, up;
low = lower_bound(nums.begin(), nums.end(), target);
up = upper_bound(nums.begin(), nums.end(), target);
vector<int> ans;
if (!binary_search(nums.begin(),nums.end(),target))
{
ans.push_back(-1);
ans.push_back(-1);
} else
{
ans.push_back(low - nums.begin());
ans.push_back(up - nums.begin() - 1);
}
return ans;
}
};LeetCode 153. Find Minimum in Rotated Sorted Array
Suppose an array sorted in ascending order is rotated at some pivot unknown to you beforehand.
(i.e.,
0 1 2 4 5 6 7might become4 5 6 7 0 1 2).Find the minimum element.
You may assume no duplicate exists in the array.
一个本来有序的数组旋转了一下,变得整体无序,部分有序了。在这样的一个旋转后的数组里查找最小值。
本质上还是可以用二分来做。就是在思考判断是否找到isFind以及向左走还是向右走的时候需要再加以修改。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38class Solution {
public:
int findMin(vector<int>& rotateArray) {
if (!rotateArray.size())
return 0;
if (rotateArray.size() == 1)
return rotateArray[0];
int len = rotateArray.size();
if (rotateArray[0] < rotateArray[len - 1])//没有旋转
return rotateArray[0];
int low = 0, high = len - 1;
int mid;
while (low <= high)
{
mid = (low + high) / 2;
if (isFind(rotateArray, mid))
return rotateArray[mid];
else if (rotateArray[mid] >= rotateArray[0])
low = mid + 1;
else
high = mid - 1;
}
return 0;
}
bool isFind(vector<int> nums, int index)
{
if (index == nums.size() - 1)
return nums[index] < nums[index - 1];
else if (index == 0)
return nums[index] < nums[nums.size() - 1];
else
return nums[index] < nums[index + 1] && nums[index] < nums[index - 1];
}
};LeetCode 154. Find Minimum in Rotated Sorted Array II
Follow up for “Find Minimum in Rotated Sorted Array”:
What if duplicates are allowed?Would this affect the run-time complexity? How and why?
Suppose an array sorted in ascending order is rotated at some pivot unknown to you beforehand.
(i.e.,
0 1 2 4 5 6 7might become4 5 6 7 0 1 2).Find the minimum element.
The array may contain duplicates.
相比上一道题就是只加了一个条件:允许重复值。但是这时候我就按照我自己的二分查找思路以及找不到如何做了。因为在a[mid] == a[0] 的时候你可以往左走,也可以往右走。根本二分不了。看了解答才发现可以用high = high - 1 来缩小查找的范围,把二分log(n)变成了O(n)的了。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24class Solution {
public:
int findMin(vector<int> &array)
{
int low = 0;
int high = array.size() - 1;
int mid;
while (low < high)
{
mid = low + (high - low) / 2;
if (array[mid] > array[high])//最小值一定在mid右边
{
low = mid + 1;
} else if (array[mid] == array[high])//最小值有可能在mid左边,也有可能在右边
{
high = high - 1;//去掉重复的,缩减范围
} else//array[mid]<array[high] => mid右边是单调,mid是右边最小得数,也可能是左边最小的数,所以high = mid,而非high = mid-1
{
high = mid;
}
}
return array[high];
}
}; 但是后来我又用最笨的O(n)查找的算法提交了以下发,发现耗时更短。上面的是12ms,用下面的线性查找反而是6ms。性能提升了一倍。所以,可能是有重复还不如不用二分,因为最小值可能在mid左边也有可能在右边,并不能缩减范围,用线性查找吧。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12class Solution {
public:
int findMin(vector<int> &array)
{
int minNum = INT32_MAX;
for (auto i:array)
{
minNum = min(minNum, i);
}
return minNum;
}
};
完!